|
|
|
REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
REPRODUCTION
It is ability of living organisms to produce young ones of their own kind. Following are the two main types of reproduction.
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION

Reproduction which doesn't involve fusion of male and female gamete is called asexual reproduction. Following are some important modes of asexual reproduction.
FRAGMENTATION
In this type of reproduction parent body is broken into many small fragments each fragment develop into a new individual.
EXAMPLE
The spirogyra and ulothrix reproduction take place by fragmentation.
BUDDING
Bud is unicellular or multicellular outgrowth which develops laterally on parent body. It is detached from the parent body and develop into a new individual.
EXAMPLE
Hydra and yeast.
FISSION
It is the most common method of asexual reproduction. It takes place in unicellular organisms. Parent cell is divided into two or more cells.
a) BINARY FISSION
Parent cell divides into two cells.
b) MULTIPLE FISSION
Parent cell divides into many cells.
EXAMPLE
Amoeba, paramecium and most of the unicellular organisms reproduce by fission.
REGENERATION
Development of new organisms from the broken part of the body of an organism.
EXAMPLE
It is well developed in sponges and star fish.
SPORE FORMATION

Spores are reproductive cells contain deploid number of chromosomes. They are surrounded by protective covering which protect them from infavourable conditions. Spores are capable to produce new individual when favourable conditions are available.
EXAMPLE
Fungi and plasmodium reproduce by spores.
GRAFTING
It is an artificial technique of asexual reproduction. In this method different variety of plant are grafted onto the stem of healthy young plant. The grafted branch is called scion and the stem on which branch is grafted is called stock.
EXAMPLE
Mango
CUTTING
Healthy cuttings of plant are placed in soil. The root system is developed on the lower side. After some time this cutting is developeed into a new plant.
EXAMPLE
Rose
LAYERING
This type of asexual reproduction is observed in shrubs. Shrubs grow as bush and some times branches of these shrubs get buried in soil. Thin buried part is called layer. New roots are developed from layer and axial part develops into shoot. Thus if connection between layer and parent plant is cut the layer can give rise to a new plant.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Reproduction which involves fusion of male and female gamete is called sexual reproduction.
STRUCTURE OF BISEXUAL FLOWER

Pedicel is the stalk of the flower. The disc where all whorls of the flower are arranged is thalamus or receptacle.
Following are the whorls of flower from outside to inside.
1. CALYX
It is the outermost whorl of the flower. It consist of many green leaves called sepals.
2. COROLLA
It is the second whorl of the flower. It consist of bright coloured petals.
3. ANDROECIUM
This is third whorl of the flower and a male reproductive part. It consist of many stamens. Each stamen has two parts called anther and filament.
4. GYNOECIUM
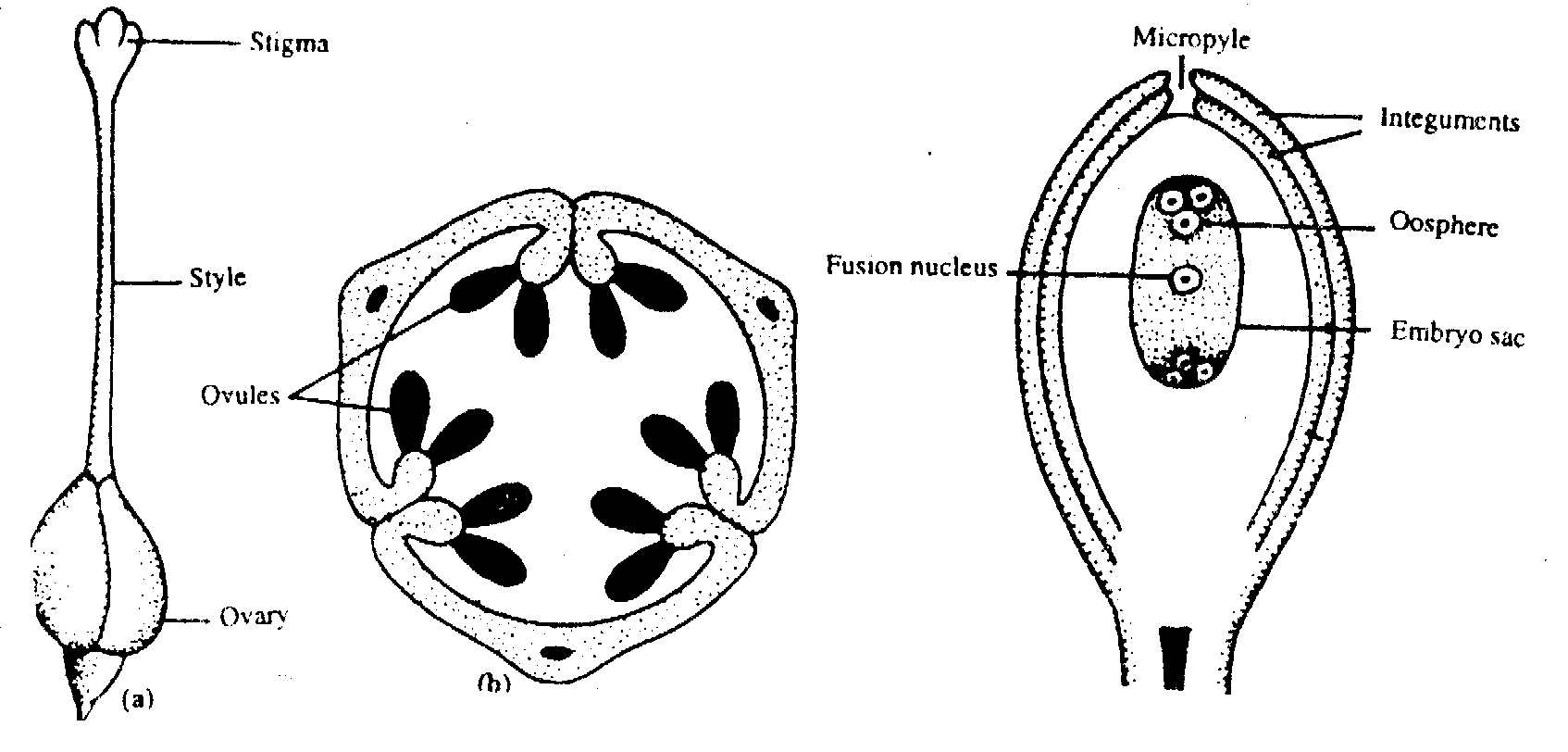
It is the innermost whorl and female reproductive part. It consist of pistal or carpel. Each pistol or carpel is mode up of three parts
Ovary contains ovule.
POLLINATION
It is the transference of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of the flower.
TYPES OF POLLINATION
Following are the types of pollination.
1. SELF POLLINATION
Transference of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of the same flower.
2. CROSS POLLINATION
Transference of pollen grains from anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower.
AGENCIES OF POLLINATION
Following are the agencies of pollination.
i. POLLINATION BY WIND
Plants having very light weight pollen grains transfer their pollen grains to another flower through wind. E.g., grass, maze.
ii. POLLINATION BY WATER
In aquatic plants pollination takes place through water. Flowers of these plants are submerged in water.
iii. POLLINATION BY ANIMALS / INSECTS
Plants having beautiful flower with fragrance and nectar transfer their pollen grains to another flower by animals or insects. E.g., china rose.
FERTILIZATION
It is the process of fusion of male and female gametes. After pollination following processes take place for preparation of fertilization and after fertilization.
FORMATION OF FRUITS AND SEEDS WITHOUT FERTILIZATION
1. PARTHENOCARPY
Development of ovary into fruit without fertilization is called parthenocary. E.g., banana, seedless grapes and guava.
2. APOMIXIS
In many flowering plants there is no reduction division and fertilization in ovule. Embryos are formed in different ways. Some times they are formed from unfertilized egg and some times from cells other than egg.
FUNCTIONS OF FRUIT
Fruit serve two main functions.
1. PROTECTION OF SEED
Particularly important when fruit is eaten by animals.
2. DISPERSAL OF SEED
DISPERSAL OF FRUITS AND SEEDS
The process by which seeds and fruits are carried from one place to another is called dispersal of fruits and seeds.
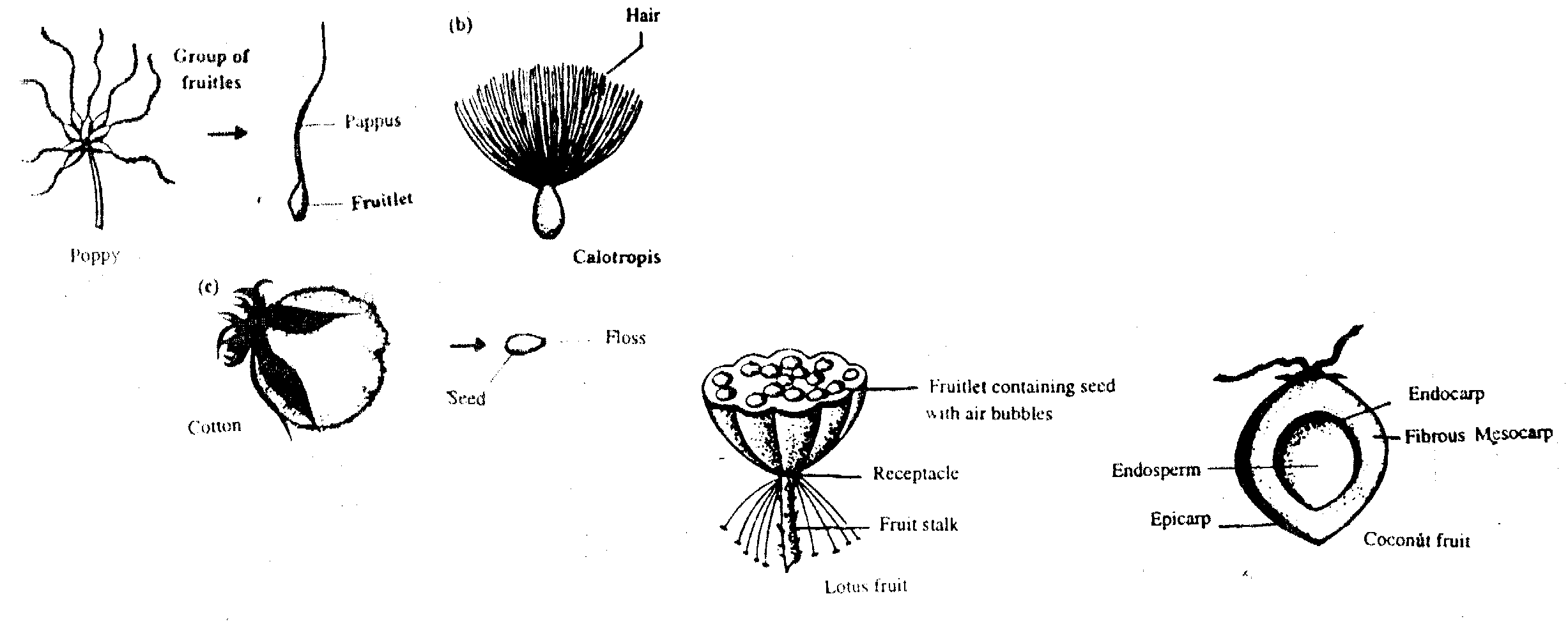
METHODS OF DISPERSAL OF FRUITS AND SEEDS
1. DISPERSAL BY WIND
Plants having small and light seeds and fruits disperse their seeds and fruits by wind. E.g., calotropis.
2. DISPERSAL BY WATER
It is the most common method of dispersal. It is usually seen in aquatic plants or in those plants which are near to water. E.g., water lily.
3. DISPERSAL BY ANIMALS
Some fruits and seeds have hooks. Fruits and seeds cling to the bodies of the animals and animals transfer them from one place to another.
Some fruits are edible and are eaten by animals and seeds are thrown away.
4. DISPERSAL BY EXPLOSIVE MECHANISM
Some fruits explode and disperse their seeds in surrounding area. E.g., lady finger, cucumber.
STRUCTURE OF TYPICAL SEED
EXTERNAL STRUCTURE
Seed is covered by seed coat. There is small opening in seed called micropyle through which seed absorbs water.
INTERNAL STRUCTURE
For convenience seed can be divided into following parts.
i. SEED COAT
The outer hard part is testa while inner coat is called tegman.
ii. ENDOSPERM
It contain stored food which is utilize by embryo during development.
iii. EMBRYO
Embryo consist of plumule, radicle and cotyledons.
a) PLUMULE
It develop to form shoot.
b) RADICLE
It develop to form root.
c) COTYLEDON
These are leaf like structures.
STRUCTURE OF CASTOR OIL
It is oval in shape and brown in colour. It is dicotyledonous seed.
EXTERNAL STRUCTURE
1. CARANCLE
It is knob like outgrowth at one end of seed. It has spongy tissues which absorb water.
2. HILUM
It is small depression near caruncle.
3. MICROPYLE
The small opening on one side of hilum is called micropyle
INTERNAL STRUCTURE
It consist of following parts.
i. SEED COAT
Seed coat consist of two layers the outer one is testa while the inner one is tegmen.
ii. ENDOSPERM
Inside the seed coat there is a food reserve in the form of albumen.
iii. EMBRYO
Embryo consist of plumule, radicle and cotyledon.
a) PLUMULE
It develop to form shoot.
b) RADICLE
It develop to form root.
c) COTYLEDONS
There are two cotyledons which come out after germination of seed and for short period of time performs the function of photosynthesis.
GERMINATION OF CASTOR SEED
GERMINATION
It is the process of activation of dormant embryo. Germination of castor seed involves following steps.
First moisture is absorbed by caruncle and water enter into the seed through micropyle. When it reach to the tegmen it rupture this covering. Finally it reach to endosperm and embryo. Water bring dissolve oxygen to embryo. Embryo starts to germinate. The radicle produces root and plumule produces shoot.
CONDITIONS NECESSARY FOR GERMINATION
Following are the conditions necessary for the process of germination.
a) WATER
Water makes seed soft and bring dissolve oxygen to the embryo.
b) OXYGEN
The germinating seeds receive oxygen for respiration.
c) SUITABLE TEMPERATURE
The process of germination is controlled by number of enzymes which works at specific range of temperature. The best temperature for germination is between 28° C to 37° C.
TYPES OF GERMINATION
1. EPIGEAL GERMINATION
The germination in which cotyledon comes above the surface due rapid growth of hypocotyle. E.g., castor seed germination.
2. HYPOGEAL GERMINATION
The germination in which cotyledons remain under the soil and plumule (shoot) comes above the soil due to rapid growth of epicotyle.
LIFE HISTORY OF PLANTS
Higher plants complete their life history by passing through two stages.
1. SPOROPHYTES GENERATION
The phase of life in which plant has diploid number of chromosomes and it produces spores (Spores are unicellular structures which can give rise to new individual without fertilization). Spores have diploid number of chromosomes.
2. GAMITOPHYTE GENERATION
In this phase of life history plants has haploid the number of chromosomes and it produces haploid gametes. These gametes fuse to form new sporophyte. In this way plant passes from sporophyte and gametophyte generation. This phenomenon is called alternation of generation.
PROPAGATION OF PLANTS BY MAN
VEGETATIVE REPRODUCTION (ARTIFICIAL PROPAGATION)
It is an artificial mode of reproduction which takes place through vegetative parts. Vegetative reproduction is faster and give rise to exact copies of selected high quality plant. Methods of vegetative reproduction.
TISSUE CULTURE TECHNOLOGY
In this method embryonic tissues of selected plants are cultured using their ability of asexual reproduction in test tube or dishes. Hormones are added to speed up growth. The new plants so produced are free from disease and are transferred to field for large commercial scale production of vegetable and crop varieties.
REPRODUCTION IN ANIMALS
There are two modes of reproduction in animals
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Mode of reproduction which doesn't involve fusion of male and female gametes.
TYPES OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Reproduction which involves fusion of male and female gametes.
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN AMOEBA
Amoeba reproduce asexually by fission. Fission is the process of splitting of parent cell into two (binary fission) or more than two (multiple fission) cells. Normally it reproduces by binary fission but during unfavourable conditions it reproduces by multiple fission.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Sexual reproduction involves fusion of male and female gametes which are produced by gonads i.e. testes and ovaries.
GAMETOGENESIS OR FORMATION OF GAMETES
The process of formation of gametes is called gametogenesis.
OOGENESIS
It is the process by which ova are formed. It involves following steps.
SPERMATOGENESIS
It is the process of formation of sperms. It involves following steps.
THE SPERM
It consist of head, neck and tail. Head contain nucleus. It is motile.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FROG
During breeding season, the male and female frog go to pond for mating. The female frog lays eggs in water and male sheds spermatozoa on eggs.
1. FERTILIZATION
It is the process of fusion of male and female gametes. Zygote is the product of fertilization.
2. CLEAVAGE
The zygote undergoes repeated mitotic division. This process is called cleavage.
3. MOULER
This is 32- 64 celled stage in which its appearance is like a irregular ball.
4. BLASTULA
It’s a stage in which a cavity called blastocoll is developed.
5. GASTRULA
After blastula next stage is gastrula. In this stage blastocoll disappears and new cavity called archentron is formed. Many layered embryo is converted into three layered embryo. The three layers are ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. These layers are called germinal layers.
FATE OF THREE GERMINAL LAYERS
ECTODERM
Ectoderm forms nervous system and outer part of the skin.
MESODERM
Develops into muscles, skeleton, circulatory, excretory and reproductive system.
ENDODERM
Endoderm forms the alimentary canal and associated organs like liver and pancreas. Endoderm also develops into lungs.
HATCHING
The development continues and the embryo now acquires elongated shape. The sheath covering the embryo breaks and larva hatched out. This is a free swimming creature and is known as tadpole. It has head, body and tail. External gills for respiration. It is herbivorous and feed on algae.
METAMORPHOSIS
These are entire post hatching changes through which tadpole larva is passed to attain more or less an adult frog. These changes are as follows.
|
Copyright © 2001 Epoint web center. All Rights Reserved. |