|
|
|
LIFE PROCESSES FOOD & NUTRITION
NUTRITION
All living organisms require food to carry out their life processes, i.e., growth, repair and for production of energy. There are two main groups of living organisms on the base of mode of nutrition.
AUTOTROPHIC ORGANISMS
(Auto à Self, troph à feeder)
These are organisms which can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis i.e., all green plants.
HETEROTROPHIC ORGANISMS
These are organisms which can not prepare their food. They take prepared food, digest it and then utilize it after absorption i.e., animals, fungi etc. Heterotrophic organisms are further classified into three groups.
FUNCTIONS OF FOOD AND ITS COMPONENTS
NEED OF FOOD
Food fulfills the following requirements of animals.
Provide energy which is released from the food by oxidation in cellular respiration.
Provides constituents for repair and growth of cells, tissues and organs.
Provides essential materials to make enzymes which are biological catalysts.
Provide materials to maintain various processes of life including reproduction.
NUTRIENTS
The food which living organisms need composed of following.
1. CARBOHYDRATES
These are organic compounds which mostly contain elements such as carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. As the name indicate carbohydrates are hydrated carbons. Each molecule contain hydrogen and oxygen in the ration of 1:2.
CLASSIFICATION OF CARBOHYDRATES
Carbohydrates have been classified into following.
MONOSACCHARIDES
Those which consist of only single unit of simple sugar e.g., glucose, fructose, galactose.
DISACCHARIDES
Those which consist of two units of simple sugar jointed together by bond between them e.g.,
lactose à glucose + galactose
maltose à glucose + glucose
POLYSACCHARIDES
Those which consist of many simple sugar jointed together by bond e.g., starch, cellulose, glycogen.
FUNCTIONS OF CARBOHYDRATES
SOURCES OF CARBOHYDRATES
Plants prepare their own carbohydrates. In man's diet carbohydrates are found in sweet fruits, jam, honey, potato, rice, bread etc.
2. FATS
Most of fats are made up of unit called triglyceride which is composed of 1 glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acid molecules.
FUNCTIONS
SOURCES
Examples of fatty food are butter, oils, ghee etc. Plants can prepare fats themselves.
3. PROTEIN
Proteins are complex organic compound consist of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur. Protein is made up of small units called amino acids.
COMPOSITION
Proteins are made up of smaller units called amino acids. There are 20 kinds of amino acids.
FUNCTIONS
SOURCES
Proteins are found in egg albumen, meat, beans and milk.
4. VITAMINS
Vitamins are essential organic compounds which are needed by our body in very small amount to maintain the normal living processes.
Some selected vitamins are described below.
VITAMIN A
Vitamin A is necessary for healthy epithelium and for rhodoposia (pigment of red cells).
SOURCES
It is found in milk, fish liver oil, carrots, sweet potatoes, tomato etc.
DEFICIENCY DISEASES
VITAMIN B
It is a complex of 12 different vitamins (B1 - B12).
SOURCES
These vitamins are found in wheat grains, milk, eggs, meat and fresh vegetables.
DEFICIENCY DISEASES
VITAMIN C
Chemical name of vitamin C is ascorbic acid.
IMPORTANCE
It is necessary for healthy skin and proper healing.
SOURCES
It is found in citrus fruits, fresh vegetables and milk.
DEFICIENCY DISEASES
Acute deficiency of vitamin C cause bleeding of gums. The disease is called scurvy.
VITAMIN D
Vitamin D is needed for the development of strong bones. It helps in absorption of calcium which makes bones hard.
SOURCES
It is present in fish liver oil and also made in our body by sunlight.
DEFICIENCY DISEASES
The deficiency of vitamin D in children causes the legs to become bowed.
VITAMIN E
It is needed for fertility.
SOURCES
It is found in green vegetables and certain seeds.
DEFICIENCY DISEASES
Deficiency of vitamin E cause sterility in some animals.
VITAMIN K
It helps in clotting of blood.
SOURCES
It is found in liver and also produced by intestinal bacteria.
DEFICIENCY DISEASE
Deficiency of vitamin K leads to inability of clotting.
5. MINERALS
There are naturally occurring inorganic compounds. Few important minerals are listed below.
CALCIUM
SOURCES
Milk, cheese, eggs, fruits, green vegetables and almond.
PHOSPHOROUS
SOURCES
It is found in fish, oysters, eggs, milk and cheese.
SODIUM, POTASSIUM AND CHLORIDE
They occur in body fluids. They are needed for regulation of functions of nerve and muscles.
IRON
It is essential for the formation of heamoglobin.
FLUORIDE
It help to prevent tooth decay.
IODINE
It is needed for normal functions of thyroid gland.
6. WATER
It is essential constituent of cytoplasm, about 70% of most tissues consist of water.
7. ENZYMES
Enzymes are biological catalyst which regulate different biochemical reactions. All biochemical reaction need enzymes to take place. Enzymes are responsible for chemical digestion of the food.
NUTRITION IN PLANTS
Modes of nutrition in plants. Plants have been classified into following groups according to the mode of nutrition.
AUTOTROPHIC
They can prepare their own food by photosynthesis.
HETEROTROPHIC
They cannot manufacture their own food. They are further classified into following groups.
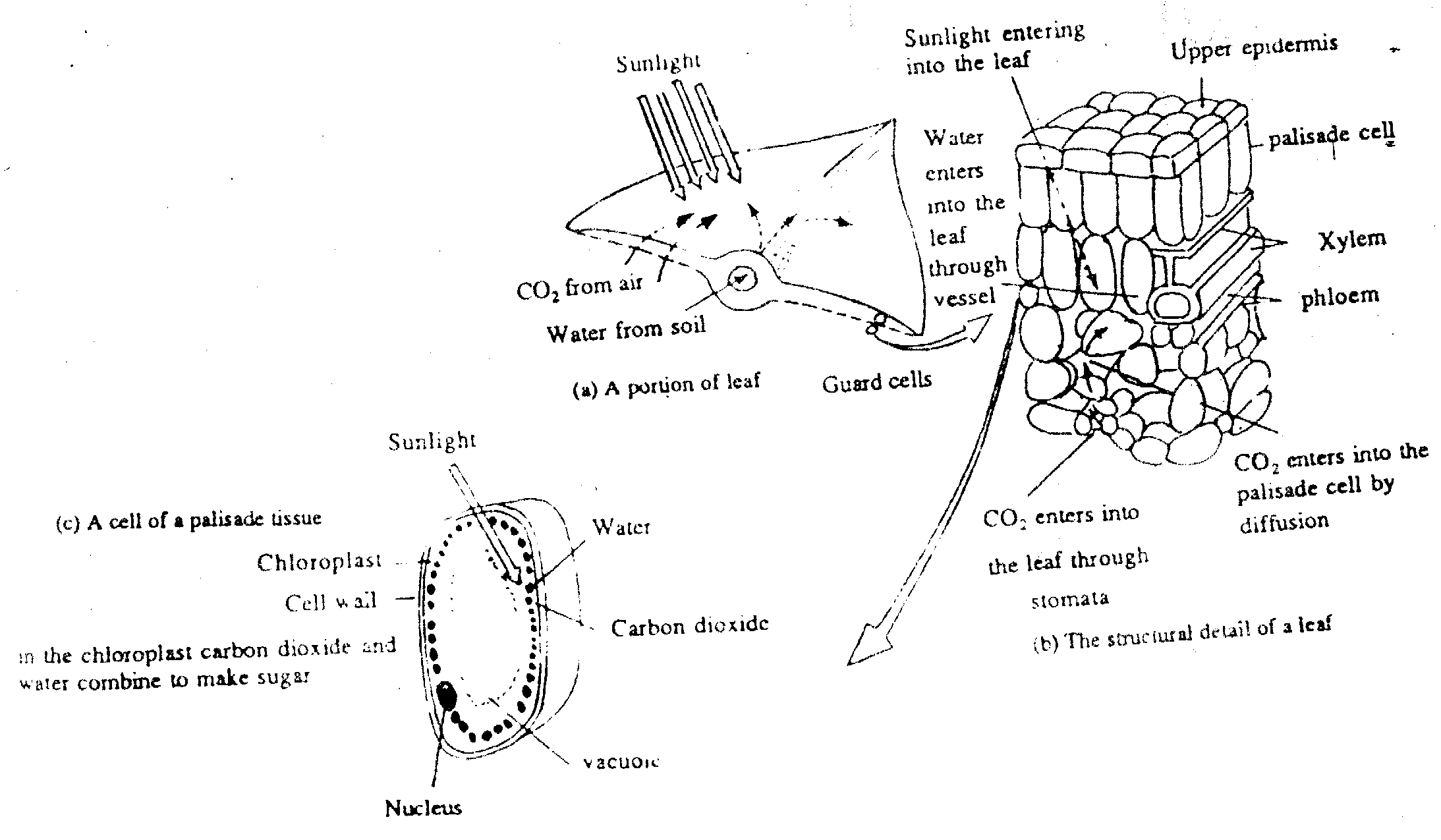
NUTRITION IN GREEN PLANTS
It is the process by which green parts of the plant prepare their food from carbon dioxide and water with the help of sunlight.
6 CO2 + 6 H2O à C6H12O6 + 6 O2
ESSENTIAL CONDITIONS AND MATERIALS FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS
1. LIGHT
Light plays following important effects.
Provides heat energy.
By the addition of photon water molecule is splitted into H+ and OH- which results in release of electrons. This process is called photolysis.
2. CHLOROPHYLL
It is green colour matter which is responsible for trapping the sunlight. When light is absorbed by chlorophyll it break water molecule into H+ and OH- and release electrons.
3. WATER
It is raw material for the process of photosynthesis. The hydrogen of water molecule becomes a part of glucose.
4. TEMPERATURE
Photosynthesis is a biochemical reaction, many enzymes are involved in this process. For the normal activities of the enzymes suitable temperature is needed. The temperature which is ideal for the process of the photosynthesis is optimum temperature. The least temperature below which photosynthesis does not take place is minimum temperature and the highest temperature above which photosynthesis does not take place is maximum temperature.
MECHANISM OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
The process of photosynthesis can be divided into following stages.
1. LIGHT REACTION
Light is necessary for this stage of photosynthesis. The light which is absorbed by chlorophyll is used to break water molecule into H+ and OH- and emission of electrons. Energy is produced by the movement of electrons which is used in the formation of ATP. The product of light reactions is ATP and NADPH2.
2. DARK REACTION
Light reaction is followed by dark reaction. The products of light reaction are used as a reactant in the dark reaction of the photosynthesis. The first stable product of the dark reaction is glucose, which is then converted into starch and other compounds.
EXPERIMENTS ON PHOTOSYNTHESIS
The first stable product of photosynthesis is glucose which is then converted into starch. Presence of starch shows that the process of photosynthesis has taken place.
STARCH TEST
OBJECT
This test is performed to check the presence of starch. It consist of following steps.
METHOD
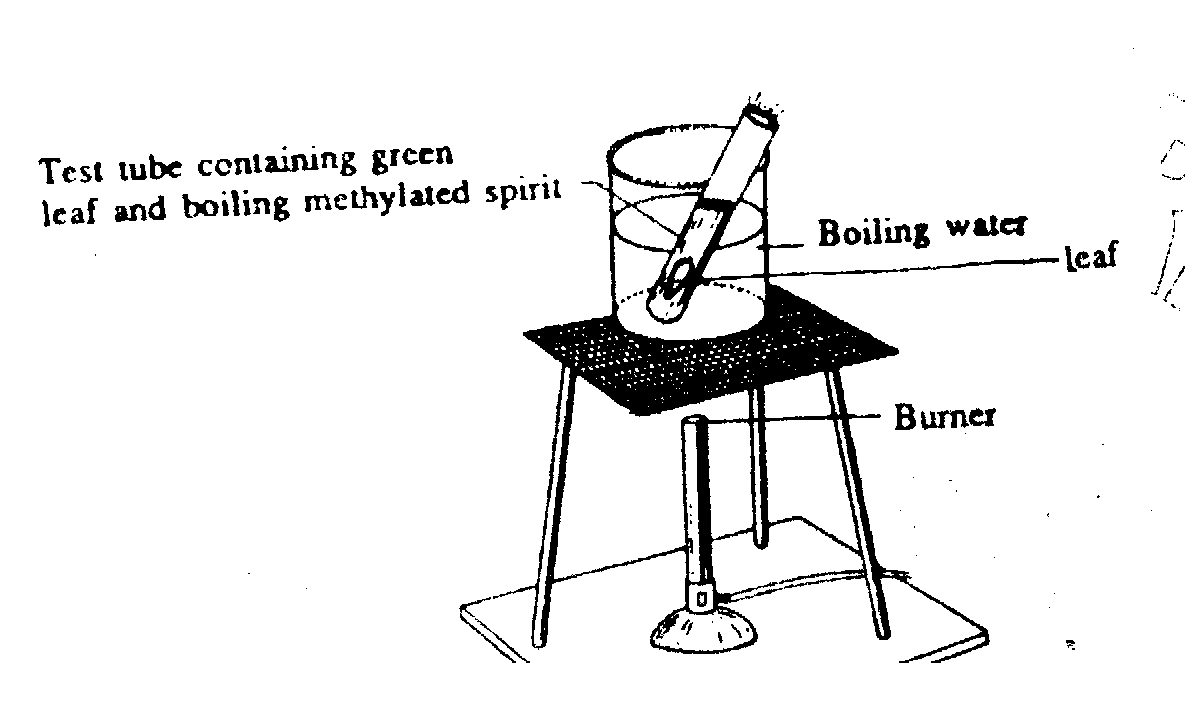
OBSERVATION
The whole leaf becomes blue.
RESULT
Blue colour shows that starch is present in the leaf because iodine reagent gives dark blue colour with starch.
EXPERIMENT NO. 1
AIM
To prove that chlorophyll is necessary for the process of photosynthesis.
METHOD
Take a potted plant having varigated leaves. Destarch the plant by keeping the potted plant in dark. Wrap it in aluminium foil and expose it to the sunlight for few hours. Detach the leaf from the plant. Draw a rough sketch of the leaf. Apply iodine test on leaf, for the presence of the starch.
OBSERVATION
The test shows that the parts of the leaf which were previously green turn blue after iodine test while the white parts turn brown.
RESULT
This result indicated that starch is formed only in those parts of the leaf where chlorophyll exist. This shows that chlorophyll is necessary for the process of the photosynthesis.
EXPERIMENT NO. 2
AIM
To prove that light is necessary for the process of the photosynthesis.
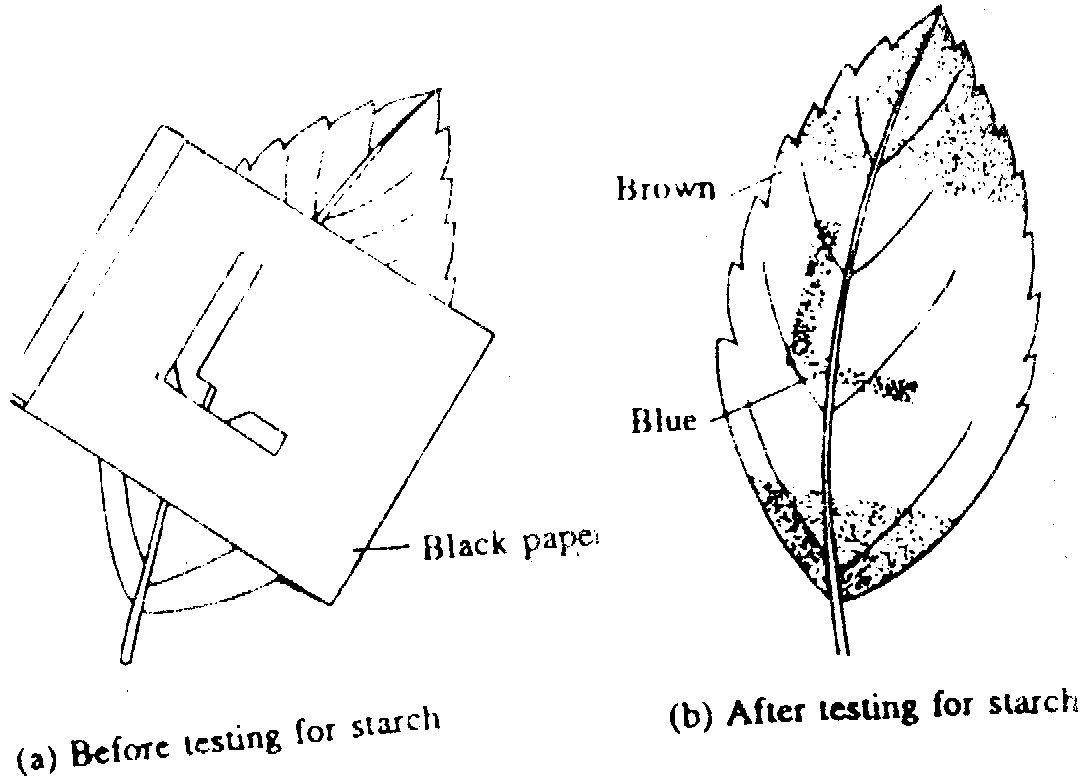
METHOD
Destarch a potted plant by keeping it in a dark room for two days. It is then transferred to light. Select two of its leaves wrap one leaf completely with black paper. Wrap another leaf with black paper but L shaped part of the paper is cut out so that light can reach the leaf through it. Place the plant in sunlight for 4 to 6 hours. Detach both leaves from the plant and perform iodine test.
OBSERVATION
It will be observed that the leaf which is covered by paper is free from the starch (remain brown with iodine). In the second leaf the area which is receiving light will turn blue while the area which is covered will remain brown.
RESULT
This shows that light plays vital role in preparation of starch, which is prepared by photosynthesis. So it is concluded from this experiment that light is necessary for the process of photosynthesis.
EXPERIMENT NO. 3
AIM
To prove that CO2 is necessary for the process of the photosynthesis.
METHOD
Destarch two potted plants by keeping them in a dark room. Water them properly during this period. Each pot is enclosed in a transparent polyethene bag. A petri dish containing soda lime is placed in one of the pots to absorb CO2. In another pot a petri dish is placed containing sodium bicarbonate solution to produce CO2. Place the plants in sunlight for few hours. A leaf from each plant is detached and tested for starch.
OBSERVATION
The leaf from the pot containing soda lime does not turn blue. The leaf from another pot will turn blue.
RESULT
This experiment shows that CO2 is necessary for the process of photosynthesis.
EXPERIMENT NO. 4
AIM
To prove that oxygen is produced during the process of photosynthesis.
METHOD
Place the short stem funnel over the aquatic plant hydrilla in a beaker of water. Place the water filled test tube over the stem of funnel. Place the apparatus in sunlight.
OBSERVATION
Bubbles of gas will soon appear from the plant and will be collected in the test tube. Remove the test tube, bring a burning match stick near the mouth of test tube. It will burn with flame vigorously.
RESULT
This shows that oxygen is produced during the process of photosynthesis as the gas in test tube is supporting the combustion.
STORAGE OF FOOD
The food prepared by the plants is used in respiration and assimilation (formation of new protoplasm). The excess amount of food is stored in different storing tissues.
VAN HELMONT EXPERIMENT
He planted willow tree which weighted 2.3 kg. After 5 years he observed that weight of tree was 2.3 kg weight of soil was 91 kg. After next five years the weight of plant become 76.9 kg and weight of soil become 90.8 kg. Increase in weight of plant was 74.6 kg and decrease in weight of soil was 2 kg.
CONCLUSION
Van Helmont concluded from this experiment that decrease in weight was due to utilization of minerals from soil and increase in weight of plant was due to absorption of water from soil by the plant.
JOSEPH PRESTLY'S EXPERIMENT
Joseph Prestly enclosed one mouse in a jar in which potted plant was present and second mouse in a jar without plant. It was noticed that the mouse in jar without plant was died due to suffocation but the mouse in jar having plant remained alive.
CONCLUSION
It was concluded by Pristly that plant take some substance from the air and replace it with a substance which is essential for the life. Later it was found that plant take CO2 from the air and give oxygen in the air.
MODE OF NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
On the basis of mode of nutrition, animals have been classified into following groups.
1. HERBIVORES
These are animals which feed on plants. E.g., elephant, cow, sparrow.
2. CARNIVORES
These are animals which feed on flesh of animals. E.g., dog, lion.
3. OMNIVORES
These are animals which feed on animals as well as plants. E.g., man, crow.
4. PARASITES
Animals which get their food from other living organisms. Parasites may be internal or external e.g., plasmodians, tape worm, ticks, mites etc.
5. SYMBIONTS
The relationship in which living organisms which are partners are mutually beneficial is called symbiosis. Such animals are called symbionts.
EXAMPLE
DIGESTION
Conversion of complex form of food into a simpler form by the action of different enzymes.
COMPLEX FORM SIMPLER FORM
Starch à Glucose
Protein à Amino acid
Fats à Fatty acid + glycerol
INGESTION
Intake of food is called ingestion
ASSIMILATION
The digested food is utilized in cellular respiration and growth. This process by which the absorbed food become a part of protoplasm is called assimilation.
EGESTION
Elimination of undigested food from the body is called egestion.
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Human digestive system has been classified into two main parts.
1. ALIMENTARY CANAL
Alimentary canal consist of following parts.
2. DIGESTIVE GLANDS
PHYSIOLOGY OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
DIGESTION IN MOUTH
Salivary glands are found in mouth. They secrete saliva which contain an enzyme called Ptyalin. Ptyalin convert starch into maltose.
Starch à Maltose
Four types of teeth are found in mouth which help to grind the food. The process is called mastication.
From mouth food is passed to the stomach through oesophagus.
DIGESTION IN STOMACH
Inner walls of the stomach posses many gastric glands which secrete gastric juice. Gastric juice contain dilute HCl, pepsin and rennin.
Dilute HCl kill bacteria, makes food soft and change the nature (pH) of food to acidic. Pepsin converts protein into polypeptide. Rennin converts milk into curd.
DIGESTION IN DUODENUM
BILE JUICE
Liver secrete bile juice which is stored in gall bladder. Bile juice is brought to the duodenum through bile duct. Bile juice contain bile salts which converts fats into tiny droplets.
PANCREAS
Pancreas secrete pancreatic juice which is alkaline in nature and contain three enzymes called trypsin, amylo trypsin and lipase. These three enzymes work along with other enzymes present in the small intestine. Pancreatic and bile juice are alkaline in nature.
ABSORPTION OF FOOD
Absorption of food takes place in ileum through villi. Villi are finger like folds of intestine lined by epithelium and provides large surface area for absorption of digested food. Absorbed food is carried to liver through hepatic portal vein and lymph vessels where it is brought to the heart.
ELIMINATION OF WASTE
Undigested food is stored in large intestine for some time and eliminated through anus.
EFFECT OF COOKING ON FOOD
ADVANTAGES
DISADVANTAGES
BALANCED DIET
The diet which contain all the nutrients in proper proportion.
Balanced diet comprise of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals. Deficiency in any group of diet results in physiological disorders.
Milk is considered to be most balanced diet for babies because it contain protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamin A, vitamin D and calcium.
DIETARY GUIDELINES
DIETARY DISORDERS
1. STARVATION
Person which doesn't get as much food as required by his body become weak, his immune system also become weak and in case of acute starvation person is starved to death.
2. MALNUTRITION
If a person taking sufficient amount of diet but missing any one or more groups of balanced diet he will suffer from certain physiological disorders.
3. FOOD ADDITIVES
They are added to the food for colouring and preservation by industries. These dyes and preservatives should be used with care.
4. FOOD POISONING
Certain harmful bacterial found in food cause food poisoning by producing poisonous substance toxic in food or by entering into the body.
|
Copyright © 2001 Epoint web center. All Rights Reserved. |