|
|
|
CHAPTER # 2
CONTROL AND COORDINATION
SENSITIVITY
Ability of living organisms to react to the change in environment. It is highly developed in higher animals. Plant also posses sensitivity but not as much developed as higher animals.
STIMULI
Any factor which cause protoplasm to react.
COORDINATION
Regulation of various activities of the body in organized manner is called coordination.
COORDINATION IN MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS
Coordination in multicellular organisms is brought by following system.
Coordination is brought about by following steps.
COORDINATION THROUGH NERVOUS SYSTEM
In all multicellular animals main types of structures related to stimuli and responses are present. These are receptors, neurons and effectors.
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF HUMAN BEINGS
Central nervous system of man consist of brain and spinal cord which contain million of special cells called neurons.
NEURONS
Neuron consist of following parts.
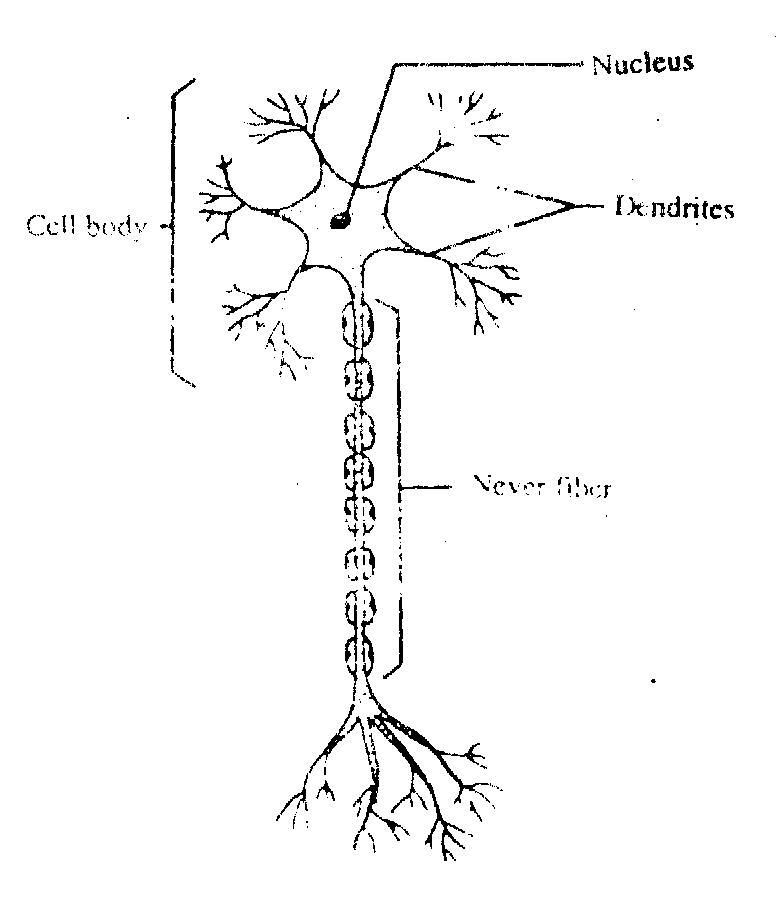
1. CELL BODY
It is rounded structure contain nucleus and other organelles.
2. CELL PROCESSES
a) DENDRITES
Many fine branches are arised from cell body called dendrites.
b) AXON
At the other end long fiber is arised from the cell body called axon.
Neurons are specialized for transmission of stimuli in the form of nerve impulse.
CLASSIFICATION OF NEURONS
Following are important types of neurons.
a) SENSORY NEURON
Neurons which carry impulses from receptors to CNS.
b) MOTOR NEURONS
Neurons which carry impulses from CNS to effectors. The peripheral effectors are muslces and glands. Muscles respond by contracting and glands by producing hormones.
Inter Neuron found in CNS, connect sensory with motor neurons.
REFLEX ACTION
It is an automatic involuntary response mediated through the central nervous system.
EXAMPLE
Withdrawal of hand immediately when touched to hot object.
Blinking of eyes on exposure to strong light.
REFLEX ARC
It is circuit of neurons through which reflex action takes place. Most of the reflex arc involve only three neurons. One of them is sensory which takes stimuli to spinal cord. Second is in CNS called inter neuron and third is motor neuron which bring message to effector.
VOLUNTARY ACTION
Action which is under the control of our will is caled voluntary action. E.g., movement of limbs.
INVOLUNTARY ACTION
Action which is not under the control of our will is called involuntary action. E.g., contraction of cardiac muscles.
BRAIN AND ITS FUNCTIONS
Human brain consist of following parts.
1. FORE BRAIN
Fore brain consist of cerebrum and aienciphalon. Cerebrum consist of two cerebral hemispheres.
FUNCTION
It is high control center of brain. Information is stored here. This part control all parts of nervous system.
2. MID BRAIN
It is located under the cerebral hemispheres.
FUNCTION
It is associated with sense of sight and hearing.
3. HIND BRAIN
Hind brain consist of cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata.
a) CEREBELLUM
It controls the body balance and movement.
b) MEDULLA OBLONGATA
It controls heart beat, respiration and circulation.
c) PONS
Transform impulses from medulla to cerebellum.
SPINAL CORD
Spinal cord is with vertebral column and continuous with medulla oblongata of brain. Spinal concerned with:
DRUGS AND NERVOUS SYSTEM
Morphine, aspirin, sleeping pills and alcohol are used in medicine to help people in getting control over pain or to feel relaxed. Frequent use (abuse) of these drugs result in certain disorders of nervous system.
Heroin, cocaine and marijuana are drugs of addiction which are being used by people to get pleasure. Many disorder of nervous system results from the use of these drugs.
SENSE ORGANS
There are five types of senses in man.
SENSE OF TOUCH
Receptors for touch are simple nerve endings which are present in through out the skin. They are specialized to detect temperature, texture, pressure etc.
SENSE OF SMELL (NOSE)
Many olfactory cells are found in nasal mincora of olfactory chamber. They are specified to receive smell stimuli.
SENSE OF TASTE (TONGUE)
Receptors for taste are groups of hair cells situated inside the flask shaped taste buds on the tongue. Their base is in contact with nerve fibers.
SENSE OF SIGHT
Human eye consist of following three layers.
a) FIBROUS COAT
It is outermost coat. It consist of
i) SCLERA
Posterior 2/3 opaque portion called sclera.
ii) CORNEA
It is exterior 1/3 of fibrous coat. It is transparent portion.
b) CHOROID
It is vescular pigmented coat. It contains many blood vessels which provide nutrition to the cells of the eye.
c) RETINA
It is the innermost layer of the eye. This is nervous coat of the eye. This layer contain rods and cones which are photoreceptors. Rods are for night vision and cones are responsible for colour vision. Rods contain rhodopsia and cones contain pigment called liopsin.
CONTENTS OF EYE BALL
1. AQUEOUS HUMOR
It is transparent fluid in front of lens.
2. LENS
It is transparent biconvex lens which converge the rays of light at retina.
3. VITROUS HUMOR
It is viscous jelly like substance present behind the lens.
4. IRIS
It project from retina.
5. PUPIL
It is an opening in the center of radial fibers of iris.
WORKING OF THE EYE
Rays of light pass from cornea to lens. Here these rays are converged and focussed at fovea centralis (point on retina where sharp image is obtained). Light stimulus is received by photoreceptors and its message is send to brain by optic nerve.
SENSE OF HEARING AND BALANCE (EAR)
Human ear consist of three portions
a) OUTER EAR
It consist of pinna, auditory canal. The outer and middle ear are separated by tympanic membrane or ear drum.
b) MIDDLE EAR
It consist of bony ossicles mellius, incus and stapes. These ossicles connected with tympanic membrane (ear drum) at the one end and at another end with inner ear.
c) INNER EAR
It consist of semicircular canals and cochlea. Receptors for hearing are located in cochlea and receptors of balance are located in semicircular canal.
WORKING OF EAR
When sound waves strike the pinna they are transferred to tympanic membrane through auditory canal. From tympanic membrane these waves are brought to inner ear through bony ossicles. When these waves are reached to cochlea receptors for hearing convert this stimulus into nerve impulse and send to the brain.
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
These are ductless glands which pour their secretion into the blood. Hormones are specific secretions of the endocrine glands. Following are important endocrine glands of man.
i. PITTUITARY GLAND
It is the master of all endocrine glands. It is located in head. It consist of two lobes. Anterior lobe of pituitary secretes seven hormones and posterior lobe secretes two hormones.
ii. THYROID
It is located in neck. It consist of right and left lobes connected by isthamus. It produces a hormone called thyroxin which control general metabolism of the body.
iii. PARATHYROID
There are two pairs of pea grain size parathyroid glands embedded in thyroid. Hormone of parathyroid gland control calcium and phosphate metabolism.
iv. PANCREAS
It measure about 7 inches in length. Pancreas produces 2 hormones.
a) INSULIN
It decrease blood sugar level by facilitating entry of glucose into the cell.
b) GLUCOGEN
It increases the blood sugar level by inducing glycogenolysis.
v. ADRENAL GLAND
There is a pair of adrenal gland, each located above the kidney. There are two regions of adrenal gland.
a) ADRENAL CORTEX
It produces cortisones and aldosterone.
b) ADRENAL MEDULLA
It produces adrenaline and non adrenaline.
vi. TESTES
It produces androgens. In this group important is testosterone which maintain male reproductive characters.
vii. OVARIES
Two important hormones are produced by ovary.
These hormones maintain normal female reproductive characters.
DISORDERS OF PITUITARY HORMONES
DISORDERS OF THYROID
Increase in secretion of thyroxin result in hyperactivity of person. Deficiency of iodine result in abnormal development of thyroid called goiter.
DISORDERS OF PANCREAS
Insulin and glucogen maintain blood sugar level. Abnormalities of pancreas result in hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
DISORDERS OF TESTES AND OVARIES
Abnormalities in testes and ovary hormone result in abnormal reproductive and sexual characters.
|
Copyright © 2001 Epoint web center. All Rights Reserved. |