|
|
|
RESPIRATION
RESPIRATION
Respiration includes following processes.
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Respiration which takes place in the cell is called cellular respiration. ATPs are produced during cellular respiration which are used as a source of energy. Following are the types of cellular respiration.
1. AEROBIC RESPIRATION
Respiration which takes place in the presence of oxygen. In this type of respiration oxygen is combined with glucose and produce carbon dioxide and water with heat energy which is used in formation of ATPs from ADP.
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 à 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + D H
2. ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION
Oxygen is not required in anaerobic respiration. It takes place in the absence of oxygen. Less amount of ATPs are produced in an aerobic respiration.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM OF MAN
Respiratory system of man consist of following parts.
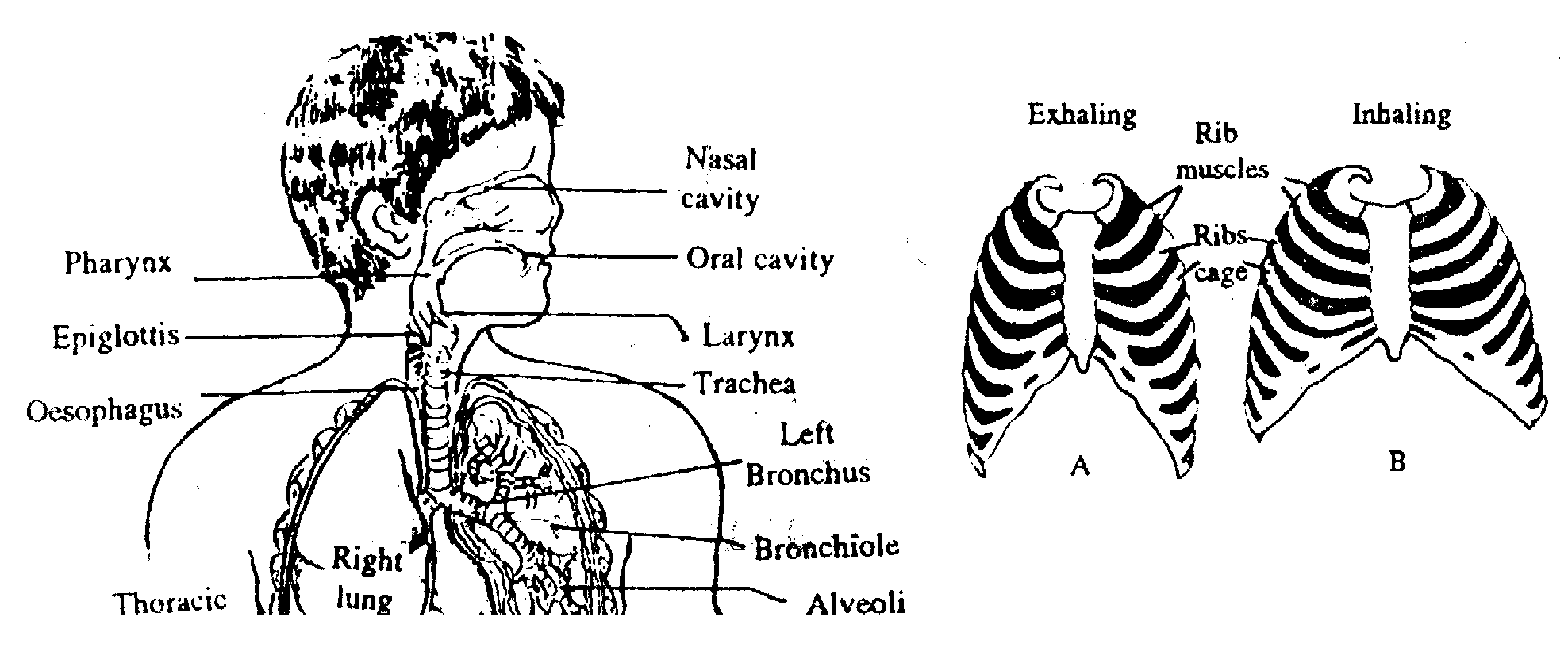
There is a pair of external nostrils outside which open into olfactory chamber. Olfactory chamber contain olfactory cells which receive stimuli of smell. Olfactory chamber opens into internal nostrils which leads to larynx. Larynx is a round box. Below the larynx there is a long tube made up of cartilages and muscles called trachea. Trachea divides into two bronchi which enter into the lungs. Lungs are made up of spongy tissues having many small air spaces called alveoli.
MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION
INSPIRATION
It is the process by which atmospheric gases are brought to the lungs.
MECHANISM
Contraction of muscles of diaphragm result in flattening of diaphragm which results in increase in volume of thoracic cavity. At the same time intercortal muscles contract which result in elevation of ribs as the result volume of thoracic cavity increase due to decrease in pressure of thoracic cavity. Atmospheric air rush into the lungs.
EXCHANGE OF GASES
In lungs exchange of gases takes place. Oxygen is absorbed in blood and CO2 is released into the lungs.
EXPIRATION
Volume of thoracic cavity is decreased by relaxation of diaphragm and intercortal muscles which results in increase in thoracic pressure and pressure of lungs. As the result air is expired from lungs to atmosphere.
TRANSPORT OF RESPIRATORY GASES
Oxygen is transported by haemoglobin contained in RBCs. While CO2 is transported through plasma and haemoglobin.
|
Copyright © 2001 Epoint web center. All Rights Reserved. |